5 Important Exercises for Regular Physical Activity

I. Introduction
A. Importance of regular physical activity
Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle and overall well-being. Engaging in regular exercise has numerous benefits that extend beyond just physical fitness. It plays a vital role in promoting mental, emotional, and social well-being. Physical issues like heart disease, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, and smoking can all cause erectile dysfunction. On the other hand, depression, anxiety, stress, relationship problems, and other mental health concerns can also interfere with sexual feelings. take super vidalista and Tadalafil dapoxetine for ED problems.
B. Benefits of exercise on overall health and well-being
- Physical health benefits:
a. Improved cardiovascular health: Regular exercise strengthens the heart and improves blood circulation, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. b. Weight management: Physical activity helps in managing weight by burning calories and increasing metabolism. c. Increased muscle strength and endurance: Engaging in strength training exercises promotes the development of lean muscle mass, enhancing overall strength and endurance. d. Enhanced flexibility and joint mobility: Certain exercises, like stretching and yoga, improve flexibility, leading to better joint mobility and reduced risk of injuries. e. Stronger immune system: Regular exercise boosts the immune system, making the body more resistant to illnesses and infections.
- Mental and emotional well-being:
a. Stress reduction: Exercise helps in managing and reducing stress by releasing endorphins, which are natural mood elevators. b. Improved mood: Physical activity stimulates the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are associated with feelings of happiness and well-being. c. Increased energy and mental alertness: Regular exercise enhances energy levels and improves cognitive function, leading to increased focus and mental alertness. d. Better sleep: Engaging in physical activity promotes better quality sleep, helping to regulate sleep patterns and reduce insomnia.
- Social benefits:
a. Increased social interaction: Participating in group exercises or team sports provides opportunities for social interaction and can foster a sense of community and belonging. b. Improved self-confidence: Regular exercise can boost self-esteem and self-confidence by enhancing physical appearance, increasing body positivity, and achieving personal fitness goals. c. Stress relief through social support: Exercise can be a social outlet and a way to connect with others, providing a support system for managing stress and emotional well-being.
In conclusion, regular physical activity offers a wide range of benefits that positively impact overall health and well-being. By incorporating exercise into daily routines, individuals can enjoy improved physical fitness, enhanced mental and emotional well-being, and increased social interaction.
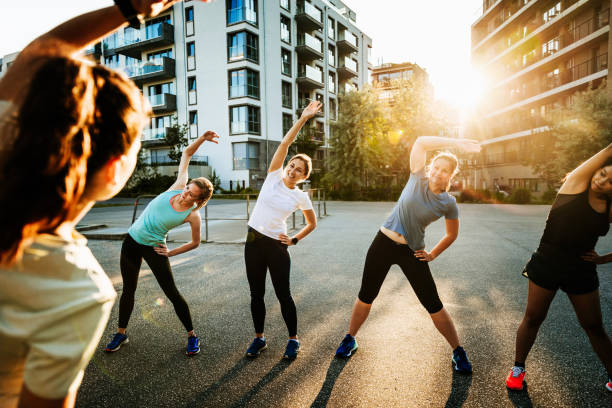
II. Exercise 1: Cardiovascular Exercise
A. Definition and benefits of cardiovascular exercise
- Definition: Cardiovascular exercise, also known as aerobic exercise, is any physical activity that increases the heart rate and engages large muscle groups for an extended period. It aims to improve the efficiency of the cardiovascular system.
- Benefits of cardiovascular exercise: a. Improved heart health: Regular cardio exercise strengthens the heart, reducing the risk of heart disease and improving overall cardiovascular function. b. Increased endurance: Cardio exercises enhance the body’s ability to use oxygen, increasing stamina and endurance levels. c. Weight management: Engaging in cardiovascular activities aids in burning calories, facilitating weight loss and weight management. d. Reduced risk of chronic diseases: Regular cardio exercise lowers the risk of developing chronic conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and certain types of cancer. e. Enhanced mood and mental well-being: Cardio exercises stimulate the release of endorphins, promoting feelings of happiness, reducing stress, and improving mental well-being.
B. Examples of cardiovascular exercises
- Running/jogging: A popular and accessible form of cardio exercise that can be done outdoors or on a treadmill.
- Swimming: A low-impact exercise that engages the entire body and provides a cardiovascular workout without putting stress on the joints.
- Cycling: Whether outdoor biking or using a stationary bike, cycling is an excellent cardiovascular exercise that improves leg strength and endurance.
- Jumping rope: A portable and high-intensity cardio exercise that can be done virtually anywhere.
- Dancing: Engaging in various dance styles, such as Zumba or aerobic dance classes, provides an enjoyable cardio workout.
C. Recommended frequency and duration of cardiovascular exercise
- Frequency: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity cardio exercise per week.
- Duration: Perform cardio exercises in sessions of at least 10 minutes, gradually increasing the duration as fitness levels improve.
D. Safety precautions and considerations
- Warm-up: Always begin with a warm-up to prepare the body for exercise and prevent injuries.
- Proper footwear: Wear appropriate shoes that provide support and cushioning for the chosen cardio activity.
- Hydration: Stay hydrated before, during, and after exercise, especially during intense cardio workouts.
- Gradual progression: Start with low-intensity exercises and gradually increase the intensity and duration to avoid overexertion or strain.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to any signs of discomfort, pain, or fatigue. If necessary, modify or adjust the intensity of the exercise.
- Consult a healthcare professional: If you have any underlying health conditions or concerns, consult with a healthcare professional before starting a new cardio exercise routine.
By incorporating cardiovascular exercise into a regular fitness regimen while following safety precautions, individuals can experience improved cardiovascular health, increased endurance, weight management, and enhanced overall well-being.
III. Exercise 2: Strength Training
A. Definition and benefits of strength training
- Definition: Strength training, also known as resistance training or weightlifting, involves exercises that target specific muscle groups to increase strength, power, and muscular endurance.
- Benefits of strength training: a. Increased muscle strength and tone: Regular strength training promotes muscle growth, leading to improved strength and a more defined physique. b. Enhanced bone health: Strength training helps increase bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. c. Improved metabolism: Building lean muscle mass through strength training boosts metabolism, aiding in weight management and fat loss. d. Injury prevention: Strong muscles and connective tissues provide better support and stability, reducing the risk of injuries, especially in joints. e. Better functional fitness: Strength training improves overall physical performance and functional abilities for daily activities.
B. Examples of strength training exercises
- Weightlifting: Using free weights or weight machines to perform exercises like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and bicep curls.
- Bodyweight exercises: Exercises that use body weight for resistance, such as push-ups, pull-ups, lunges, and planks.
- Resistance band exercises: Utilizing elastic bands to provide resistance during exercises like rows, shoulder presses, and leg extensions.
- Kettlebell exercises: Incorporating kettlebells into exercises like swings, snatches, and Turkish get-ups.
- Calisthenics: Bodyweight exercises that involve dynamic movements like burpees, mountain climbers, and handstand push-ups.
C. Importance of proper form and technique
- Correct form: Performing exercises with proper form is crucial to maximize effectiveness and minimize the risk of injury.
- Technique: Understanding and following the proper technique for each exercise ensures that the targeted muscles are engaged and worked effectively.
- Seek guidance: If new to strength training, it’s advisable to seek guidance from a certified trainer or coach to learn proper form and technique.
D. Recommended frequency and duration of strength training
- Frequency: Aim for at least two to three strength training sessions per week, allowing for adequate rest and recovery between sessions.
- Duration: Each strength training session should typically last 30 to 60 minutes, including warm-up and cool-down periods.
E. Safety precautions and considerations
- Warm-up: Prior to strength training, perform a dynamic warm-up to increase blood flow, warm up muscles, and prepare the body for exercise.
- Start with appropriate weight: Begin with lighter weights or resistance and gradually increase as strength and proficiency improve.
- Progress gradually: Avoid the temptation to lift heavy weights beyond your capabilities too quickly. Gradually increase the load to prevent injuries.
- Rest and recovery: Allow adequate rest between strength training sessions to promote muscle recovery and avoid overtraining.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to any pain, discomfort, or unusual sensations during exercise. Stop if something feels wrong and consult a professional if necessary.
- Stay hydrated: Maintain proper hydration before, during, and after strength training sessions.
By incorporating strength training into a well-rounded fitness routine while following proper form, technique, and safety precautions, individuals can experience increased muscle strength, improved body composition, enhanced bone health, and reduced risk of injuries.